The History of Artificial Intelligence
The history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a fascinating journey that spans over centuries of human thought and a few decades of technological breakthroughs. Here’s a structured overview:
📜 1. Ancient Roots & Early Concepts
Even before computers existed, humans imagined intelligent machines.
-
Ancient Myths & Legends: Stories from Greek mythology (like the mechanical servant Talos) and Jewish folklore (the Golem) reflect early ideas of artificial beings.
-
Philosophical Foundations:
-
Aristotle (4th century BC): Developed syllogistic logic — a precursor to logical reasoning in AI.
-
Ramon Llull (13th century): Tried to develop a mechanical system to combine basic truths to produce knowledge.
-
🧠 2. Foundations in Mathematics & Logic (1600s–1940s)
-
René Descartes and Gottfried Leibniz: Explored symbolic reasoning and mechanical logic.
-
George Boole (1800s): Invented Boolean algebra, essential for computer logic.
-
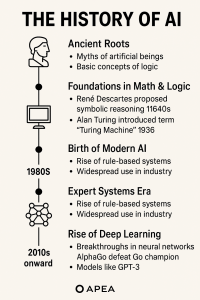
Alan Turing (1936): Proposed the Turing Machine, laying the theoretical groundwork for computers. In 1950, he introduced the Turing Test to assess machine intelligence.
💡 3. Birth of Modern AI (1950s)
-
1956 — The Dartmouth Conference: Organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon. This event marked the official birth of AI as a field. McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence.”
-
Early achievements:
-
Logic Theorist (1955): Program by Allen Newell and Herbert Simon that proved mathematical theorems.
-
Early AI programs played chess and solved algebra problems.
-
🚀 4. Early Optimism and the First AI Boom (1950s–1960s)
-
Researchers believed human-level AI was just a few decades away.
-
Development of early languages like LISP (by John McCarthy) for AI programming.
-
Limitations in computing power and unrealistic expectations led to the first AI winter (a period of reduced funding and interest).
❄️ 5. AI Winters and Limited Progress (1970s–early 1980s)
-
Hype didn’t match results; funding dried up.
-
Systems couldn’t handle real-world complexity.
-
Rule-based systems dominated but struggled to scale.
🌱 6. Expert Systems Era (1980s)
-
AI made a comeback with expert systems (e.g., MYCIN, XCON): rule-based programs that mimicked human expertise.
-
Widely used in industries.
-
Eventually hit limitations (brittle knowledge bases, high cost of maintenance), leading to another downturn.
🔁 7. Revival Through Machine Learning (1990s–2000s)
-
Shift from rule-based systems to data-driven learning.
-
Algorithms like decision trees, support vector machines, and Bayesian networks became popular.
-
Growth in computing power and digital data laid the groundwork for modern AI.
-
IBM’s Deep Blue (1997) defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov — a major milestone.
🤖 8. Rise of Deep Learning and Modern AI (2010s–present)
-
Deep Learning (neural networks with many layers) became practical due to GPUs and big data.
-
Major breakthroughs:
-
2012: AlexNet wins ImageNet competition, revolutionizing computer vision.
-
2016: Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeats Go champion Lee Sedol.
-
2020s: Explosion in natural language processing (NLP) with models like:
-
GPT-2 (2019) and GPT-3 (2020) by OpenAI
-
ChatGPT (2022) revolutionized human-like conversation
-
GPT-4 (2023) enhanced reasoning and multi-modal capabilities
-
-
⚙️ 9. Current Trends and Future Outlook
-
AI is now used in:
-
Healthcare (diagnosis, drug discovery)
-
Finance (fraud detection, trading)
-
Transportation (self-driving cars)
-
Entertainment (recommendations, content creation)
-
Education, law, agriculture, and more.
-
-
Concerns include:
-
Ethical use and bias
-
Job displacement
-
Alignment with human values (AI safety research)
-
Conclusion
Thank you for reading this article, may I know your views concerning this article on the comment section below. These shall be used to improve the performance of the site. If you are interested in more articles like this, also don’t hesitate to let us know.